However the mass of a fluid is strange to calculate since there is not necessarily a feesibly measurable amount of say water flowing through a pipe. In a horizontal tube of non-uniform cross section area water is.
The Continuity Equation Fluid Mechanics Lesson 6 Youtube Fluid Mechanics Teaching Science Physics
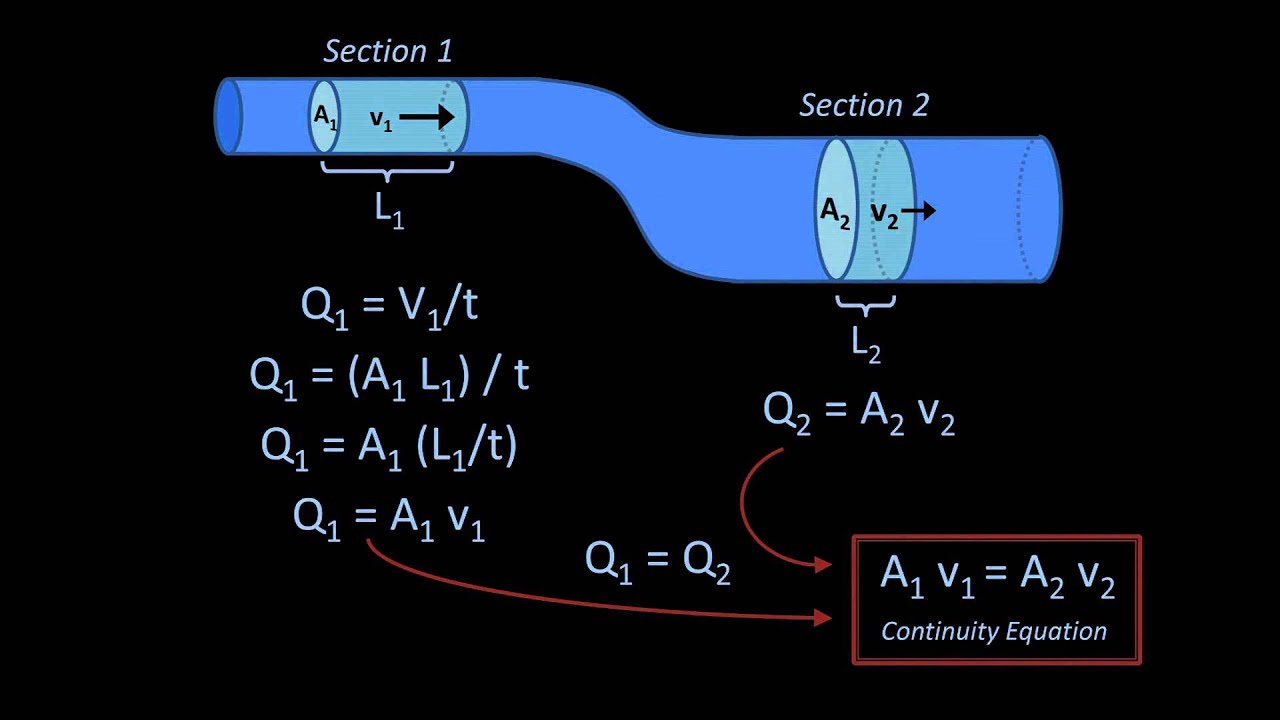
According to the principle of continuity v x A x v y A y.

. Therefore v y v x A x A y. As such relations to density ρ m V. It is particularly simple and powerful when applied to a conserved quantity but it can be generalized to apply to any extensive quantity.
12 Mass flux at an infinitesimal volume element. Consider a fluid flowing through a pipe of non uniform sizeThe particles in the fluid move along the same lines in a steady flow. Fluid pressure and depth.
V c v the control volumes velocity. We will call this a control volume and develop conservation equations for water and properties of water inside it. Water enters into a smooth horizontal tappering tube with a speed 2 msec and emerges out of the tube with a speed 8 msec.
For control volume with N inlets and outlets. The independent variables of the continuity equation are t x y and z. If the fluid is incompressible r1 r2 and the continuity equation reduces to A1 v1 A2 v2.
While the outlet flow through the pump is 9200 lbmsec. We can generalize the continuity equation for the case in which the fluid is not incompressible. It is intuitive that fluid flow speeds up as the cross-sectional area decreases as shown at the right.
V absolute velocity. Text mass flow rate frac Delta m Delta t. Through the continuity equation the behavior of fluid is described when it is in motion.
According to the law of conservation of mass. The equation of continuity gives us a way of determining the velocity of the fluid moving at point 2. In fluid mechanics the equation for balancing mass flows and the associated change in density conservation of mass is called the continuity equation.
Imagine some volume interior to the ocean surrounded by imaginary sidewalls. V y 80 ms. The continuity equation means the overall mass balance.
For any control volume Σ t whence the continuity equation. Continuity Equation Fluids Flow. Physically the integral form suggests that the continuity equation should be interpreted as relating the density at.
The continuity equation is simply a mathematical expression of the principle of conservation of mass. If we consider the flow for a short interval of time Δtthe fluid at the lower end of the pipe covers a distance Δx 1 with a velocity v 1. ρ t.
This implies that ρ 1 V 1ρ 2 V 2 and since the fluid is. The continuity equation is expressed as follows. R1 A1 v1 - r2 A2v20.
Mass flow rate ΔtΔm. Taking this into consideration equation 1 can be modified to the following. From the continuity equation A 1v 1 A 2v 2 A fv f A f A 2 A 1 v f v 1 v 2 The relative volume flow rate is V 1t 1 015 V 2t 2 m3s-1 The areas of the pipes are different A 1 3 A 2 m2.
This equation is applicable to steady compressible or incompressible fluid flows and is called Continuity Equation. By the equitation of continuity the amount of fluid moving past point 1 per unit time is the same as that moving past point 2 per unit time. The Hamiltonian operator is a spatial derivative vector.
1 ρ t ρμ where ρ is the density kgm 3 and u is the velocity vector. If the moving control volume is also non-deforming the dot product sign convection used for a non-deforming fixed control volume will apply. Or mathematically mass flow rate Δ m Δ t.
Therefore the flow velocity at y is 80 ms. The continuity equation in fluid dynamics describes that in any steady state process the rate at which mass leaves the system is equal to the rate at which mass enters a system. Eq 5 t C V ρ d V C S ρ W n d A 0.
Continuity principle refers to the principle of fluid mechanics. 1 Continuity equation for one-dimensional flows. We call the equation of continuity.
V y 10 2 25 10 2. Divide by ϵ and take the limit ϵ 0 together with Gauss theorem on the boundary term to conclude that. A simplified derivation and explanation of the continuity equation along with 2 examples.
The continuity equation is the equation of conservation of mass in a fluid flow. The continuity equation for this situation is partial v_1 over partial x_1 partial v_2 over partial x_2 0. The differential form of the continuity equation is.
The continuity equation explains this. ρ 1 A 1 V 1 ρ 2 A 2 V 2. Consider a 2-D steady state flow field of an incompressible fluid.
So this is the continuity equation for a compressible fluid. Sketch of a fluid control volume with arrows to show fluid entering and leaving through two sidewalls. For steady one dimensional flow with one inlet and one outlet.
If ρ1 and ρ2 are the densities at sections 1 and 2 then ρ 1 A 1 V 1 ρ 2 A 2 V 2. For a control volume that has a single inlet and a single outlet the principle of conservation of mass states that for steady-state flow the mass flow rate into the volume must equal. 11 Mass flux at an finite volume element.
The continuity equation can also be used to show that a decrease in pipe diameter will cause an increase in flow velocity. Fluid statics What is a fluid. Fluid dynamics - Equation of continuity and Bernoullis principle.
The principle of continuity equation is a consequence of the law of conservation of mass. Rate of flow in section 1 - 1 Rate of flow at section 2 - 2. Whereas the second equation is based on Newtons law of motion which describes the motion of an.
Σ t ρ t ρ v d V 0. Find the ratio. A continuity equation or transport equation is an equation that describes the transport of some quantity.
Continuity Equation - Centrifugal Pump The inlet diameter of the reactor coolant pump shown in Figure 3 is 28 in.

The Navier Stokes Equations Of Fluid Dynamics In Three Dimensional Unsteady Form Physics And Mathematics Engineering Science Equations

The Navier Stokes Equations Of Fluid Dynamics In Three Dimensional Unsteady Form Mathematics Worksheets Physics And Mathematics Fluid Dynamics

Fluids Lecture 2 2 Continuity And Bernoulli S Equation Youtube Physics And Mathematics Physics Fluid Mechanics

Pin On Civil Engineering Ssc Je

Experimental Thermo And Fluid Mechanics Lab 4 Fluid Kinematics 4 1 Velocity Field 4 2 Continuity Equation Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanic

Physics Formula Physics Formula En Instagram Fluid Mechanics Properties Of Matter New Chapter Form Physics Formulas Fluid Mechanics Properties Of Matter

Continuity Equation In Cylindrical Coordinates Conservation Of Mass Continuity Coordinates

Discharge And Continuity Equation Part 13 Youtube Fluid Mechanics Equation Continuity

We Have Already Seen The Derivation Of Continuity Equation Bernoulli S Equation Momentum Equation Velocity Of So Basic Concepts Stationary Fluid Flow

Venturi Effect Wikipedia Physics And Mathematics Venturi Fluid Mechanics

Steady Flow Turbulent Flow And Applications On The Continuity Equation Physics And Mathematics Basic Physics Physics Lessons

Till Now We Were Discussing The Various Concepts And Equations Such As Continuity Equation Euler Equation Bernoulli Equations Fluid Flow Math Equations

Bernoulli S Equation Energy Work Fluid Flow Civil Engineering

The Euler Equations Of Fluid Dynamics In Two Dimensional Steady Form And Incompressible Form Science Formulas Equations Physics Lessons

Mcat Physics Flashcard Continuity Of Volume Flux Illustration Fluid Mechanics Continuity Equation In The Flow Of An Idea Fluid Mechanics Physics Mechanic

Fluids Lecture 2 1 Continuity And Bernoulli S Equation Youtube Fluid Mechanics Lecture Fluid

Physics Fluid Flow 1 Of 7 Bernoulli S Equation Youtube Physics And Mathematics Fluid Mechanics Physics

Pin On Civil Engineering Ssc Je

We Have Already Seen The Derivation Of Continuity Equation Bernoulli S Equation Momentum Equation Velocity Of S Fluid Mechanics Hinges Basic Concepts
